Australia launches study into CSP deployment costs
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) has launched a request for information on all types of CSP technologies in order to define the scope and focus of government assistance for solar thermal deployment.
Government-owned ARENA has invited CSP industry participants such as developers, investors, original equipment manufacturers and offtakers, to provide information on key cost drivers and any regulatory, commercial or technical barriers to deployment.
The agency's studies will support federal government pledges for new funding in CSP plants. The federal government recently issued the state of South Australia an AU$110 million low-interest loan to build a CSP plant in Port Augusta, Nick Xenophon, Senator for South Australia, said in a statement April 1.
The new plant will provide baseload power production and will be a "flagship project for the rest of the country," he said.
ARENA has invited companies to submit by July 31 information on optimum plant sizes, storage capacities and preferred renewable energy offtake arrangements. Developers are invited to set out anticipated areas of cost reduction and supply chain benefits.
“ARENA works across the innovation chain to building a vital bridge between commercial development and uptake. These fresh efforts will seek to map out and support a pathway for [CSP] to achieve commercial viability in Australia,” Ivor Frischknecht, ARENA CEO, said in a statement.
“Our large-scale solar PV competitive round proved that the cost of renewable energy technologies can be reduced significantly with targeted efforts. We’re ready to explore whether the same success is possible for the development of [CSP] in Australia,” he said.
Site search
SolarReserve is considering developing four to six CSP plants, each of capacity 100 to 150 MW, in the Australian state of Queensland, Daniel Thompson, SolarReserve's Australia director, told the Courier Mail newspaper May 6.
The U.S.-based developer is currently scouting for sites in Queensland, particularly in the north and west of the state, Thompson said. Potential areas include Mount Isa, Roma, Moranbah and Georgetown.
Queensland is an attractive market due to its strong Direct Normal Irradiance (DNI) levels and the State government's target of producing 50% of energy from renewable sources by 2030, Thompson told the paper.
SolarReserve is in "very positive" discussions with the Queensland government and the company may apply for a concessional loan from the federal government's AU$5 billion North Australian Infrastructure Facility (NAIF) scheme, Thompson said.
SolarReserve has also reportedly proposed to build a 110 MW plant with eight hours’ storage at Port Augusta.
California renewables provide 40% of daily demand
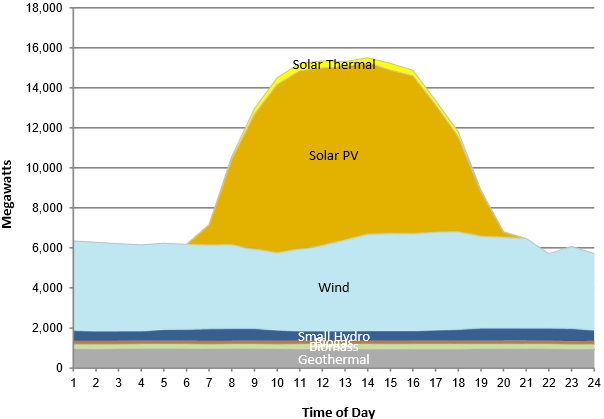
Renewable energy sources provided 238,489 MWh of power to California's grid on May 16, representing a record-high 40% of total daily power demand, data from CAISO, California's grid operator, showed.
CSP Plants provided 3,093 MWh on May 16 and peak CSP output was 365 MW at 11:36 am.
California's renewable energy production peaked at 2 pm when it provided a record 72% of grid power, according to Utility Dive magazine.
California's hourly renewables output on May 16
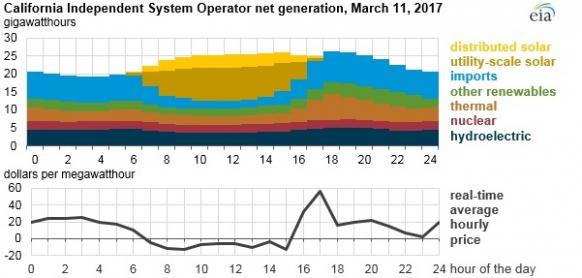
On March 11, utility scale solar power accounted for 40% of California's net grid power generation between 11 am and 2 pm, the highest level ever recorded in the state, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) said last month.
Rising solar capacity has helped lower wholesale power prices in the CAISO network into negative price territory across some daylight hours, particularly in Spring.
California power demand hits its lowest levels in late winter and early spring while solar output increases as the days grow longer and the sun gets higher in the sky. Negative prices are usually caused by conventional power generators remaining online to avoid high shutdown or restart costs.
Net generation vs wholesale prices on March 11