On September 18, the 100 MW CSP plant of the CTGR Hami 1 GW "CSP + PV" integrated demonstration project—general-contracted by Northwest Electric Power Design Institute Co., LTD, of China Power Engineering Consulting Group(CPECC Northwest), the executive vice-chairman unit of the CSTA—achieved full-system grid connection, marking the full completion of China's largest linear-Fresnel CSP-based integrated energy demonstration base.
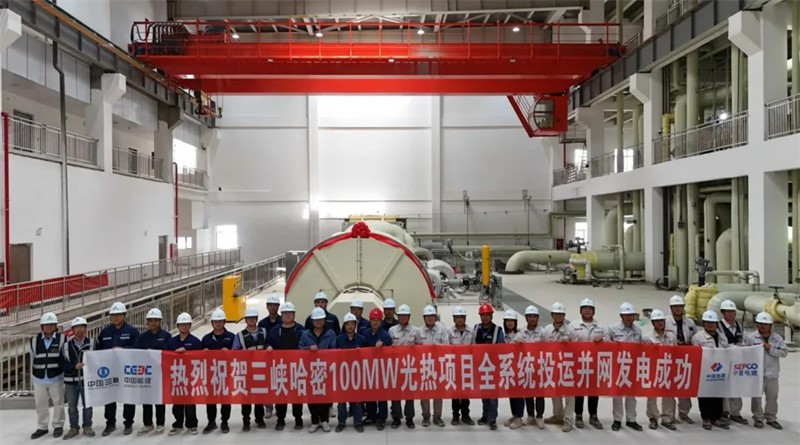

The CTGR Hami 1 million-kilowatt "CSP + PV" integrated energy demonstration project is the largest of its kind in Xinjiang. Located in Xishan Township, Yizhou District, Hami City, the project has a total installed capacity of 1 million kilowatts and is developed under an integrated "CSP + PV" model. The 100,000-kilowatt CSP plant, constructed by CPECC Northwest, is the first CSP project in Xinjiang to adopt molten salt linear Fresnel technology. It is equipped with 260,000 reflectors and has a solar field area of 800,000 square meters. The solar collection system was built by Dunhuang Dacheng Shengneng New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of Lanzhou Dacheng Technology Co., Ltd. The plant includes 8 hours of thermal energy storage.
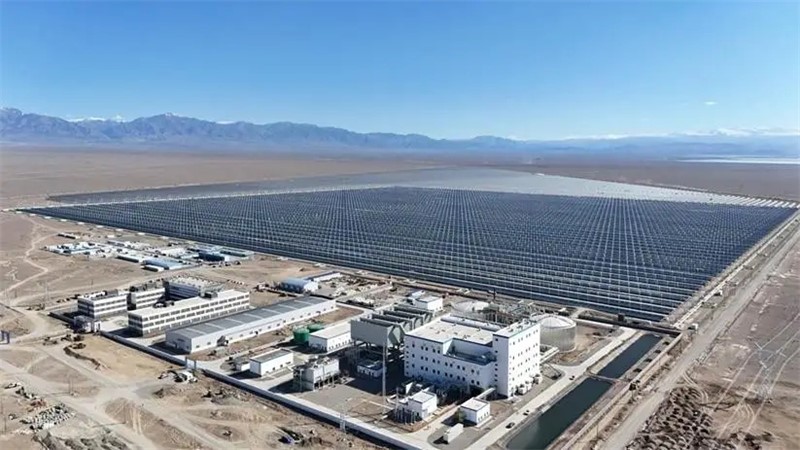

The CSP plant will operate in coordination with a 900,000-kilowatt PV plant. By leveraging the stable output characteristics of CSP, it effectively compensates for the intermittency of solar PV, enabling 24-hour continuous and stable power generation. This promotes the transformation of traditional renewable energy bases from "single intermittent sources" to "controllable, adjustable, and secure integrated energy bases," offering a significant demonstration and driving effect in overcoming bottlenecks in large-scale renewable energy development and advancing renewable energy substitution.
Once fully operational, the integrated energy base is expected to generate approximately 2.067 billion kWh of clean electricity annually, reduce carbon dioxide emissions by over 1.63 million tons, and save 620,000 tons of standard coal. While significantly enhancing the region’s renewable energy consumption capacity, it also provides a valuable reference for building a new power system centered on renewable energy.
During construction, the project successfully applied multiple optimized designs and pioneering technologies, offering key technical support for improving the reliability, cost-effectiveness, and operational efficiency of CSP plants.
1. Optimized Design for Cost and Efficiency Gains**
The CPECC Northwest design team improved the hydraulic balance of the linear Fresnel solar collection system, significantly enhancing flow uniformity across loops and solving imbalance issues at a low cost. At the same time, structural design and operational strategies for key molten salt equipment such as steam generators and molten salt storage tanks were optimized, effectively reducing equipment failure rates and improving overall plant reliability. Additionally, the cooling system for the main turbine was optimized to ensure cooling performance while greatly improving construction efficiency.
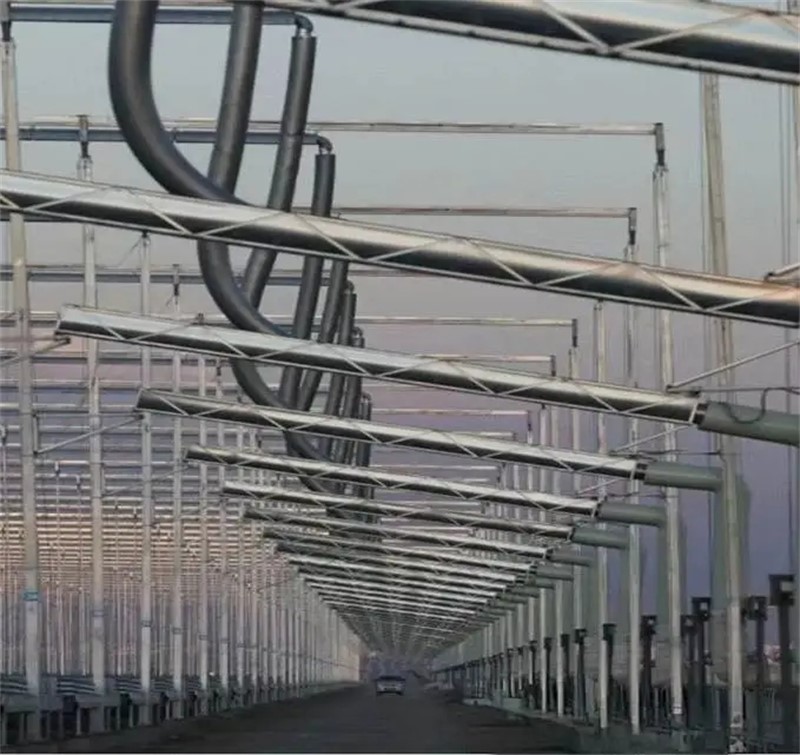

2. Integrated Control for PV + CSP
The CPECC Northwest team integrated data from two PV plants and one CSP plant into the CSP control room and the CTGR Group’s central control center. This shifted the management model from decentralized and flat to regional, intensive, and lean, significantly improving overall operational efficiency.
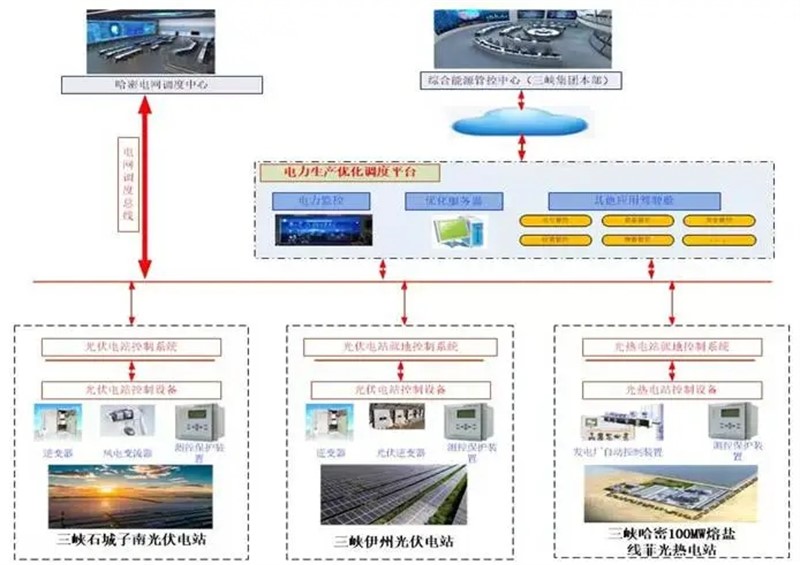
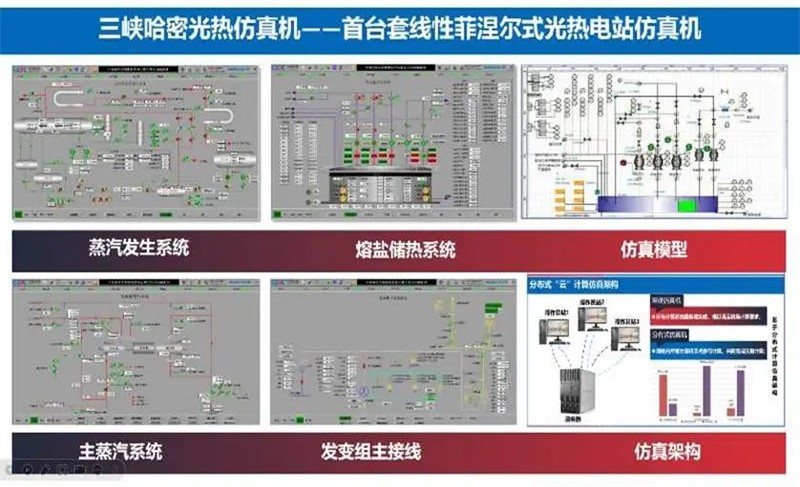
3. First-Ever Linear Fresnel Full-System Simulator
The CPECC Northwest team developed the world’s first full-system simulator for a linear Fresnel CSP plant. This will greatly enhance operator proficiency and emergency response capabilities, providing strong support for safe and efficient long-term operation.
4. First CSP Plant APS System Successfully Deployed
In collaboration with China Energy Engineering Group CENTRAL China Electric Power Testand Research Institute CO., LTD., CPECC Northwest successfully developed China’s first automatic plant start-up and shutdown (APS) system for CSP plants. Using segmented breakpoint control technology, the system allows each operational segment to function independently or in coordination, significantly reducing manual operations and the risk of human error. This greatly enhances unit safety, stability, and operational flexibility.

Since construction began in March 2024, the project implemented a series of advanced management systems, including standardized inspection checklists, dynamic scoring grids, and grid captain responsibility systems. These enabled refined operations with unified planning, checklist-based execution, and individual accountability. The project achieved full-system grid connection in just 18 months, setting a new record for the shortest construction period among similar CSP projects, fully demonstrating the industry-leading "Energy Construction Speed" and "Energy Construction Quality."


