According to the latest updates from Cosin Solar’s project site, the 100 MW solar tower unit of the Jinta Zhongguang “CSP + PV” pilot project operated continuously for three consecutive days from 13 to 15 August, delivering an average daily output exceeding 1 GWh. On 14 August alone, the plant generated 1.317 GWh—an all-time high for a plant of this type during its initial months of commercial operation.

The operating curve for 14 August shows that the CSP unit reduced its daytime load to prioritize PV generation, then ramped to full output overnight, fully realizing the design goal of complementary CSP-PV operation in large renewable-energy bases.
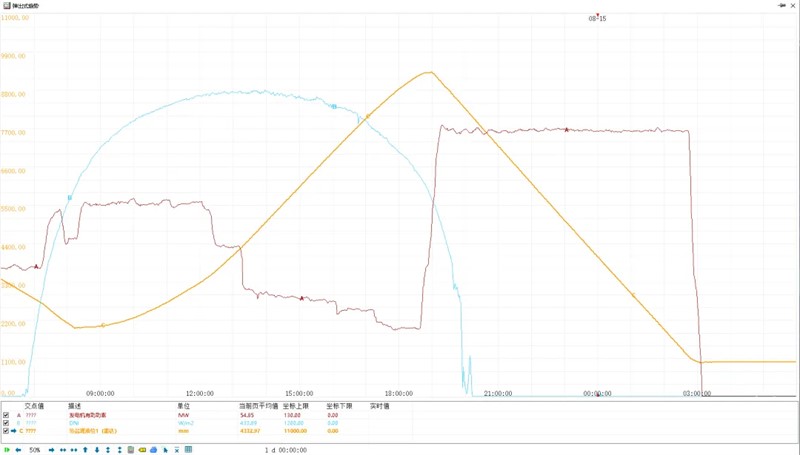
Commercial operation began on 28 May 2025, with full-process commissioning completed on 10 July 2025. Within 11 days the plant reached full-load operation, recording a single-day output of 1.024 GWh on 21 July. From 10 July to 15 August (a period that included nine rainy days and 17 cloudy days) the unit was dispatched for 26 operating days, accumulating 391.2 hours of generation and producing 15.548 GWh in total.
Thanks to the joint efforts of Cosin Solar and China Green Development (Gansu), the entire system has achieved stable operation without a single fault-induced outage since full-process commissioning. Notably, the plant’s first-of-its-kind low-level-tank short-shaft molten-salt pump system is performing above design expectations: vibration at the cold-salt pump’s rated flow is below 0.3 mm/s, and the minimum level in the cold-salt tank has reached below 0.5 m—far superior to conventional high-level-tank designs and significantly improving salt-utilization efficiency.
During daylight hours the plant also operates electric salt heaters to absorb surplus PV power, enhancing overall economic performance. This engineering validation of CSP-PV synergy through molten-salt electrical heating lays a solid foundation for future large-scale deployment.
Project Overview

Located in the Baishuiquan PV Industrial Zone, Jinta County, Jiuquan City, the Jinta Zhongguang “CSP + PV” pilot project is part of the second batch of China’s large-scale desert, Gobi and wasteland renewable-energy bases. Total installed capacity is 700 MW, configured as 600 MW of PV and 100 MW of CSP with 8 hours of molten-salt storage and a 767,800 m² heliostat field. Once fully operational, the project is expected to deliver 1.45 TWh of clean electricity annually, saving ~480,000 t of standard coal and reducing CO₂ emissions by ~1.36 million t each year—providing significant benefits for local socioeconomic development and energy conservation.


