
Highlights
-
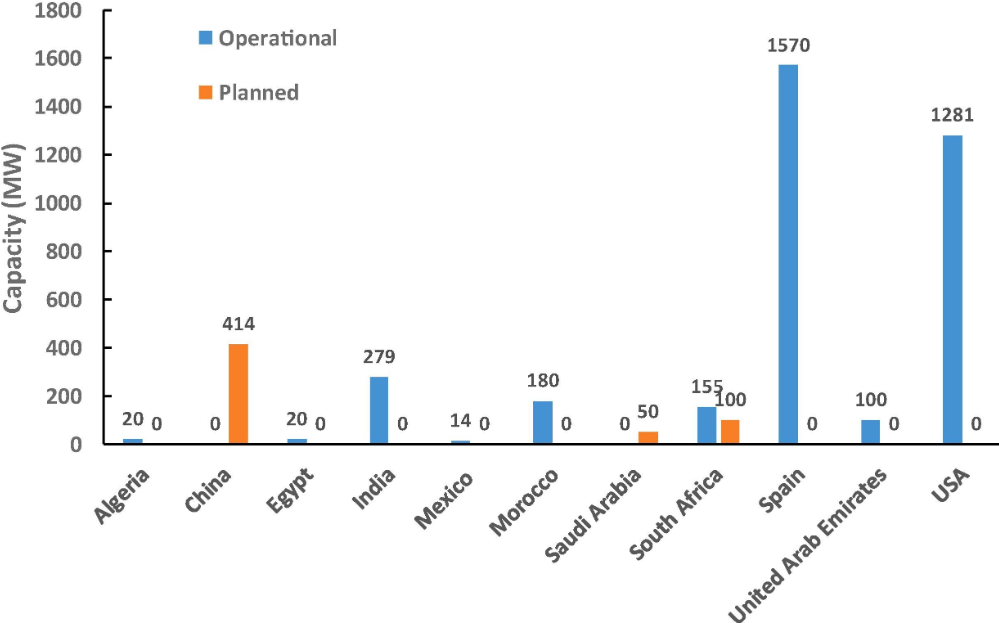
Developed photovoltaic retrofit for concentrating solar thermal power plants. -
Concentration ratio on receiver of 74 during experiment (93 with model). -
Average efficiency of 21.3% based on measured flux to photovoltaic modules. -
LCOE estimated below 7¢/kWh for photovoltaic retrofit on existing facilities.
Abstract
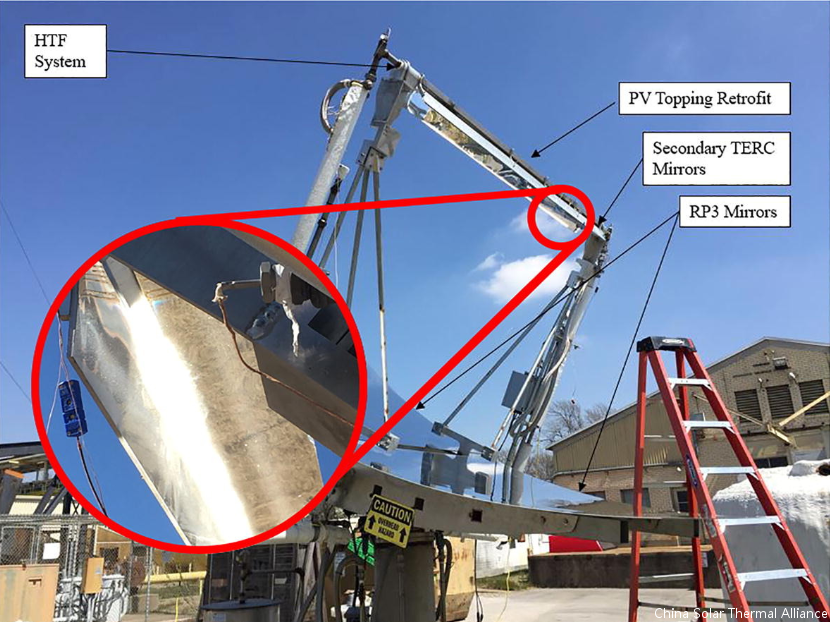
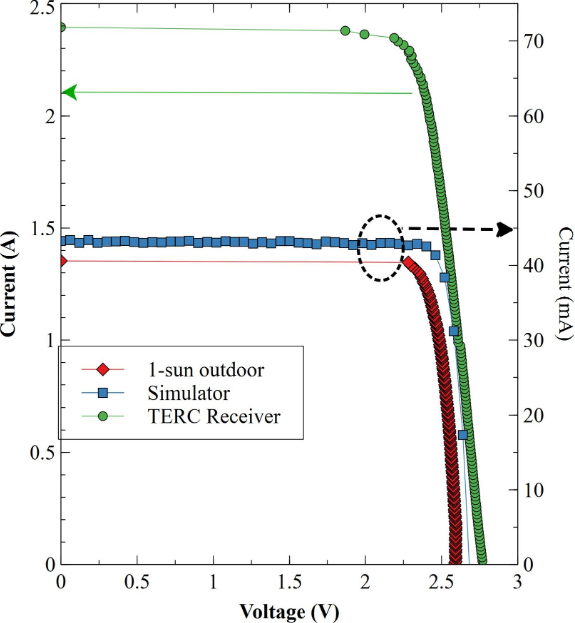
Photovoltaics and concentrating solar thermal power are two ways for generating electricity from sunlight, albeit through different methods. Parabolic trough style powerplants represent 3.6 GW of electricity production, but many of these plants are aging and being replaced with photovoltaics. An alternative option that could be employed to leverage the sunk capital cost associated with the primary optics would be the design of a pure photovoltaic retrofit working within the existing plant architecture. Here, a secondary optical concentrator is designed to use the existing primary optics of a parabolic trough type solar thermal powerplant. The design is a v-shaped secondary concentrator resulting in a predicted concentration ratio on a 20 mm wide target of 94. The concentrating photovoltaic receiver for retrofit of an RP-3 based parabolic trough has been constructed using multi-junction concentrator photovoltaic cells and experimentally demonstrated here for the first time. Calculated performance of the cells based on cell specifications should result in 31% efficiency at 85 °C. On-sun efficiencies were measured at an average value of 21% with operational temperatures between 55 and 120 °C. Levelized cost of electricity calculations predict the system to have the potential to be below 7 ¢/kWh based on predicted efficiencies and 13 ¢/kWh based on the measured values at cell costs of 5 $/cm2.
Keywords
-
Photovoltaic (PV)
-
Concentrating solar power (CSP)
-
Solar energy
-
Retrofit
Schematics

https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261920302634#f0050


